This is a very early release of server-timings module, intended as an Express middleware.
Firstly you need to load the middleware as early as possible to record the request timing:
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const timings = require('server-timings');
app.use(timings);
app.use(require('./routes'));
This will automatically add a Server-Timing header shown in milliseconds (note that in stable Chrome shows timings in seconds, this will change):
$ curl https://jsonbin.org/remy/urls -I
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Server-Timing: 0=72.45; "Request"
To include additional timings the middleware exposes two methods on the res.locals.timings property:
start(label) - record the start timeend(label) - end the record time - if this isn't called, it will be called when the request is finishedAs well as being exposed in res.locals.timings you can also call start and end as middleware:
app.use(timings);
app.use(timings.start('routing'));
app.use(require('./routes'));
app.use(timings.end('routing'));
See jsonbin.org for a working example. As of March 2017, the networking timings can be seen in Canary:
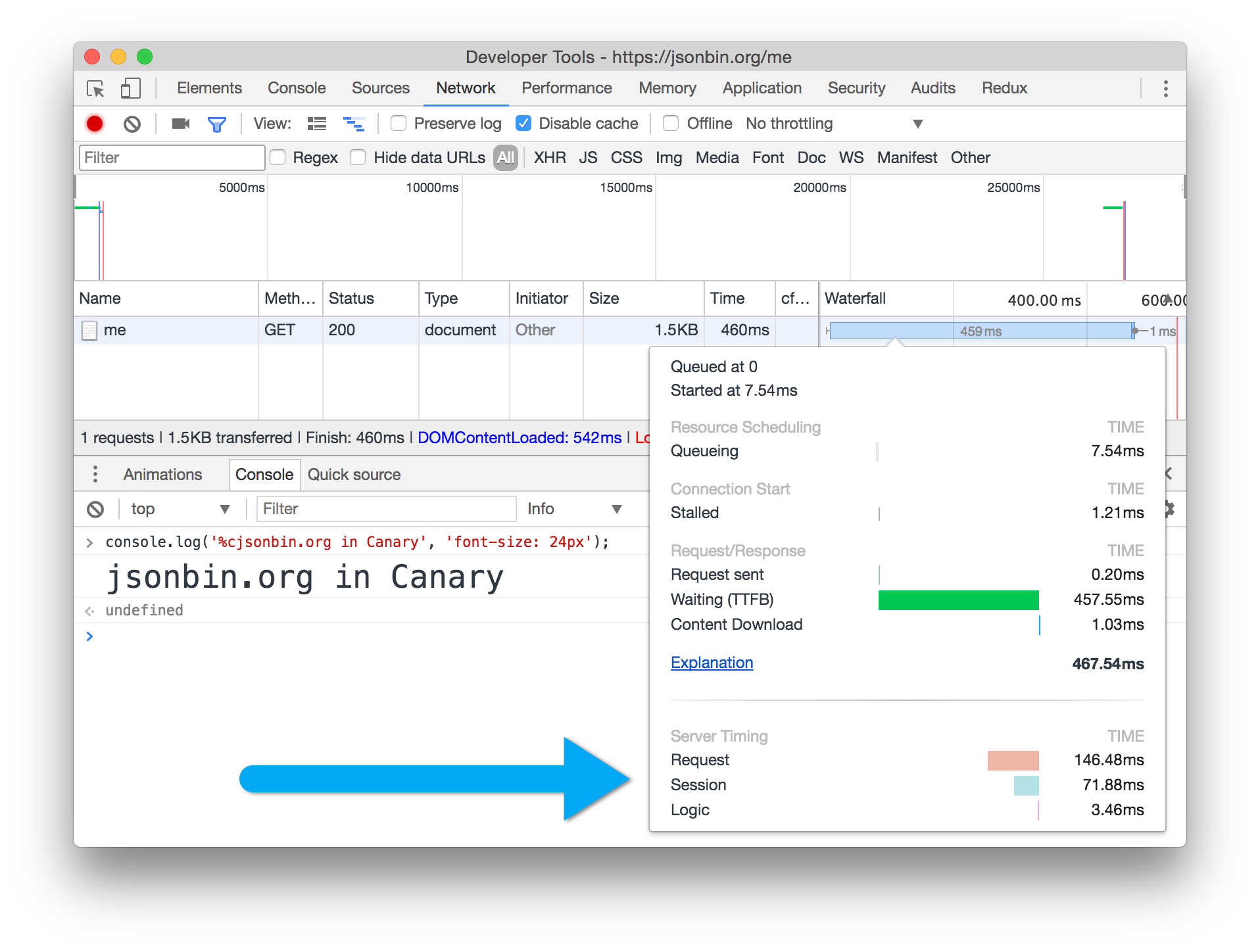
next() so limited to Express